Page 410 - Bank Muamalat_AR24
P. 410
408 BANK MUAMALAT MALAYSIA BERHAD
BASEL II
PILLAR 3 DISCLOSURE
8.4 LIQUIDITY RISK
Liquidity and Funding Risk
Liquidity risk is best described as the inability to fund any obligation on time as they fall due, whether due to increase in
assets or demand for funds from the depositors. The Bank will incur liquidity risk if it is unable to create liquidity and this
has serious implication on its reputation and continued existence.
In view of this, it is the Bank’s priority to manage and maintain a stable source of financial resources towards fulfilling the
above expectation. The Bank, through active balance sheet management, ensures that sufficient cash and liquid assets
availability are in place to meet the short and long term obligations as they fall due.
Generally, liquidity risk can be divided into two types, which are:
• Funding Liquidity Risk
Refers to the potential inability of the Bank to meet its funding requirements arising from cash flow mismatches at a
reasonable cost.
• Market Liquidity Risk
Refers to the Bank’s potential inability to liquidate positions quickly and insufficient volumes, at a reasonable price.
As stated in the policy, the Bank’s liquidity risk magnitude segregated into the following:
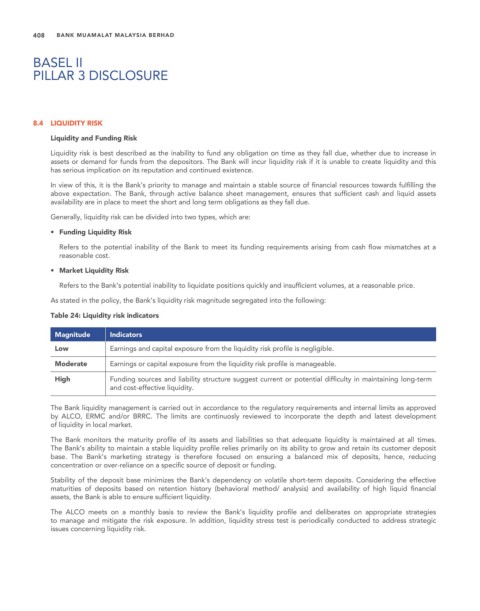
Table 24: Liquidity risk indicators
Magnitude Indicators
Low Earnings and capital exposure from the liquidity risk profile is negligible.
Moderate Earnings or capital exposure from the liquidity risk profile is manageable.
High Funding sources and liability structure suggest current or potential difficulty in maintaining long-term
and cost-effective liquidity.
The Bank liquidity management is carried out in accordance to the regulatory requirements and internal limits as approved
by ALCO, ERMC and/or BRRC. The limits are continuosly reviewed to incorporate the depth and latest development
of liquidity in local market.
The Bank monitors the maturity profile of its assets and liabilities so that adequate liquidity is maintained at all times.
The Bank’s ability to maintain a stable liquidity profile relies primarily on its ability to grow and retain its customer deposit
base. The Bank’s marketing strategy is therefore focused on ensuring a balanced mix of deposits, hence, reducing
concentration or over-reliance on a specific source of deposit or funding.
Stability of the deposit base minimizes the Bank’s dependency on volatile short-term deposits. Considering the effective
maturities of deposits based on retention history (behavioral method/ analysis) and availability of high liquid financial
assets, the Bank is able to ensure sufficient liquidity.
The ALCO meets on a monthly basis to review the Bank’s liquidity profile and deliberates on appropriate strategies
to manage and mitigate the risk exposure. In addition, liquidity stress test is periodically conducted to address strategic
issues concerning liquidity risk.